Root Canal Treatment
“Endo” is the Greek word for “inside” and “odont” is Greek for “tooth.” Endodontic treatment treats the inside of the tooth.
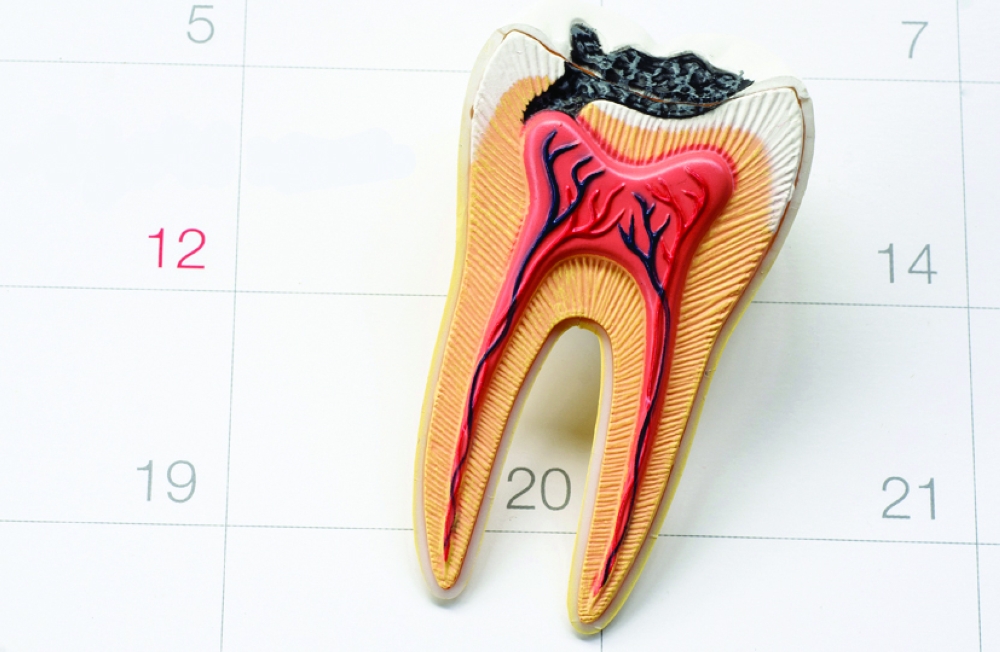
To understand endodontic treatment, it helps to know something about the anatomy of the tooth. Inside the tooth, under the white enamel and a hard layer called the dentin, is a soft tissue called the pulp. The pulp contains blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue and creates the surrounding hard tissues of the tooth during development.
The pulp extends from the crown of the tooth to the tip of the roots where it connects to the tissues surrounding the root. The pulp is important during a tooth’s growth and development. However, once a tooth is fully mature it can survive without the pulp, because the tooth continues to be nourished by the tissues surrounding it.
Endodontic treatment is necessary when the pulp, the soft tissue inside the root canal, becomes inflamed or infected. The inflammation or infection can have a variety of causes: deep decay repeated dental procedures on the tooth or a crack or chip in the tooth. In addition, an injury to a tooth may cause pulp damage even if the tooth has no visible chips or cracks. If pulp inflammation or infection is left untreated, it can cause pain or lead to an abscess.
Signs to look for include pain, prolonged sensitivity to heat or cold, tenderness to touch and chewing, discoloration of the tooth, and swelling, drainage and tenderness in the lymph nodes as well as nearby bone and gingival tissues. Sometimes, however, there are no symptoms.
The endodontist removes the inflamed or infected pulp, carefully cleans and shapes the inside of the canal, a channel inside the root, then fills and seals the space. Afterward, you will return to your dentist, who will place a crown or other restoration on the tooth to protect and restore it to full function. After restoration, the tooth continues to function like any other tooth.
You should not chew or bite on the treated tooth until you have had it restored by your dentist. The unrestored tooth is susceptible to fracture, so you should see your dentist for a full restoration as soon as possible. Otherwise, you need only practice good oral hygiene, including brushing, flossing, and regular checkups and cleanings.
Most endodontically treated teeth last as long as other natural teeth. In a few cases, a tooth that has undergone endodontic treatment does not heal or the pain continues. Occasionally, the tooth may become painful or diseased months or even years after successful treatment. Often when this occurs, redoing the endodontic procedure can save the tooth.
New trauma, deep decay, or a loose, cracked or broken filling can cause new infection in your tooth. In some cases, the endodontist may discover additional very narrow or curved canals that could not be treated during the initial procedure.
Most teeth can be treated. Occasionally, a tooth can’t be saved because the root canals are not accessible, the root is severely fractured, the tooth doesn’t have adequate bone support, or the tooth cannot be restored. However, advances in endodontics are making it possible to save teeth that even a few years ago would have been lost. When endodontic treatment is not effective, endodontic surgery may be able to save the tooth.